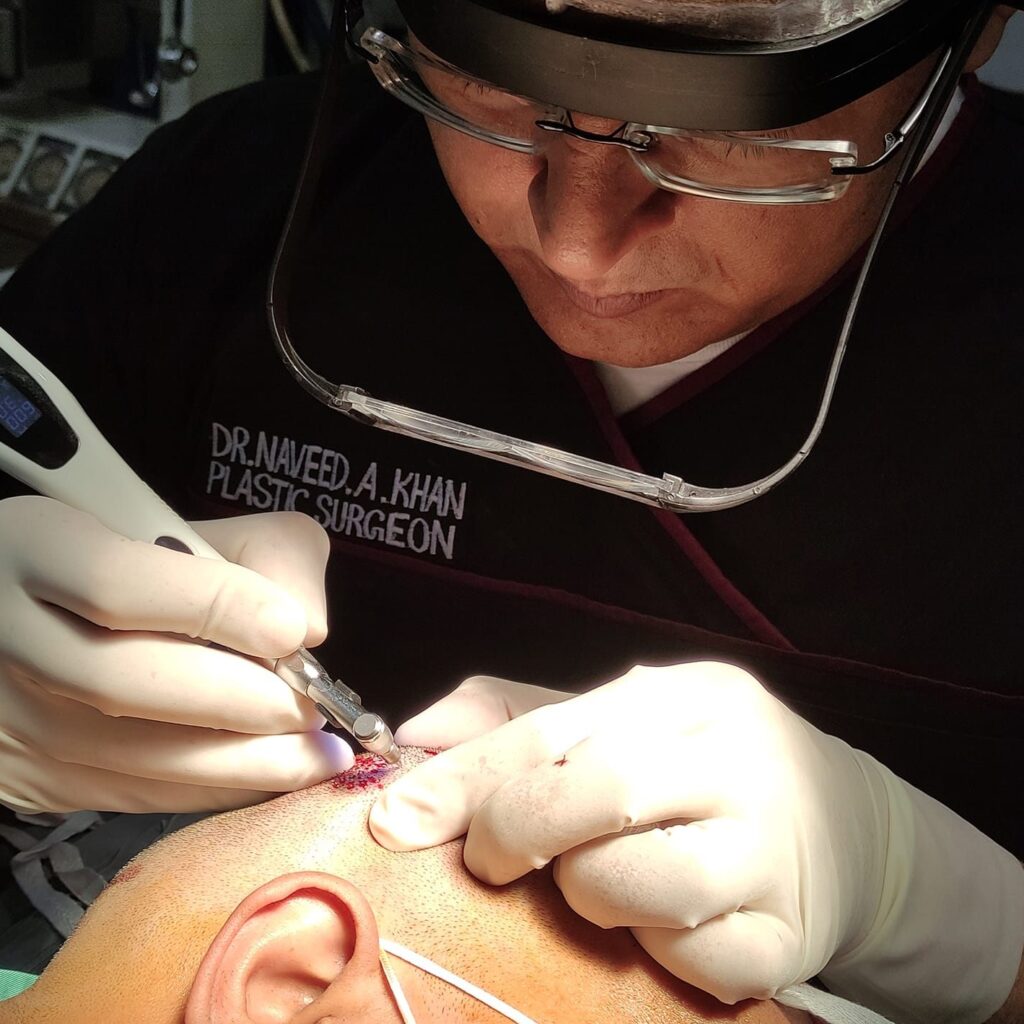
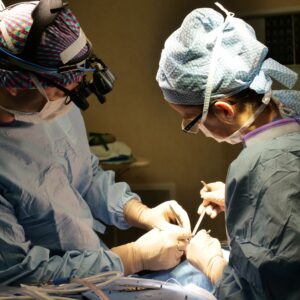
 Hand reconstructive surgery, also known as hand surgery, is a specialized form of plastic surgery that focuses on restoring or improving the function and appearance of the hand, wrist, and forearm. Hand reconstructive surgery is usually performed for medical reasons, such as injuries, congenital conditions, or degenerative diseases. Although hand reconstructive surgery can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life, it is not without its risks and complications.
Hand reconstructive surgery, also known as hand surgery, is a specialized form of plastic surgery that focuses on restoring or improving the function and appearance of the hand, wrist, and forearm. Hand reconstructive surgery is usually performed for medical reasons, such as injuries, congenital conditions, or degenerative diseases. Although hand reconstructive surgery can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life, it is not without its risks and complications.
- One of the most common risks of hand reconstructive surgery is infection. The hand is a highly exposed and delicate area of the body, and it is therefore prone to infections. A minor infection can cause serious complications, including sepsis, tissue death, and even amputation. To minimize the risk of infection, patients must practice good hand hygiene, and keep the surgical wound clean and dry.
Another potential risk of hand reconstructive surgery is nerve damage. The hand is richly supplied with nerves, and even minor nerve damage can result in sensory changes, such as numbness or tingling, and motor changes, such as weakness or paralysis. To minimize the risk of nerve damage, patients must choose a highly experienced and skilled surgeon who has a good track record of performing successful hand reconstructive surgeries. - Blood clots, also known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), are another potential complication of hand reconstructive surgery. DVT can occur when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the leg, which can then travel to the lungs and cause a potentially life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. To minimize the risk of DVT, patients must be encouraged to move around as soon as possible after surgery, and to wear compression stockings.
- Wound dehiscence, which refers to the separation of a surgical wound, can also occur after hand reconstructive surgery. Wound dehiscence can result in painful wound openings, scarring, and an increased risk of infection. To minimize the risk of wound dehiscence, patients must follow the surgeon’s post-operative instructions, and avoid activities that put excessive stress on the surgical wound, such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercise.
- Finally, hand reconstructive surgery can also result in scarring. Scarring can be unsightly and can impair the function and appearance of the hand. To minimize the risk of scarring, patients must use silicone gel sheets or silicone gels, which can help to reduce the visibility of scars and improve their texture and appearance.
- In conclusion, hand reconstructive surgery can be a highly effective way of restoring or improving the function and appearance of the hand, wrist, and forearm. However, it is not without its risks and complications, including infection, nerve damage, DVT, wound dehiscence, and scarring. To minimize these risks and complications, patients must choose a highly experienced and skilled surgeon, practice good hand hygiene, follow the surgeon’s post-operative instructions, and use silicone gel sheets or gels to reduce scarring. If you are considering hand reconstructive surgery in Pakistan, it is important to choose a highly qualified and experienced surgeon who can help to ensure a successful outcome
- American Society for Surgery of the Hand: https://www.assh.org/handcare/hand-anatomy
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/reconstructive-procedures/hand-surgery
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/hand-surgery
- Journal of Hand Surgery: https://www.jhandsurg.org/
- The Journal of Hand Surgery: European Volume: https://journals.sagepub.com/home/jhs
- Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/hand-surgery/about/pac-20395034
- Hand Surgery & Rehabilitation Journal: https://www.journals.elsevier.com/hand-surgery-and-rehabilitation
- British Society for Surgery of the Hand: https://www.bssh.ac.uk/patients/hand-conditions/
- The Journal of Hand Therapy: https://www.jhandtherapy.org/
- Hand Clinics Journal: https://www.hand.theclinics.com/